Marvelous Tips About Do Houses Use Series Or Parallel Circuits

Illuminating the Truth
1. Why Understanding Circuits Matters
Ever wondered how all your lights and appliances can work at the same time without dimming or causing a complete blackout? It's all thanks to the way your home's electrical system is wired. Hint: it's not like those old Christmas lights where one bulb goes out and the entire string dies a slow, agonizing death. (Okay, maybe not agonizing, but definitely annoying!). Let's dive into the electrifying world of circuits and uncover whether your house operates on series or parallel connections.
The electrical system in your house is a carefully orchestrated network designed to deliver power efficiently and safely. If you're thinking about doing some electrical work yourself, remember that working with electricity can be dangerous. It's always best to consult a qualified electrician for any major projects or repairs. Safety first, always!
The type of circuits used in your home has a direct impact on how your electrical system functions. It determines how power is distributed, how devices are affected by changes in the circuit, and how easily problems can be isolated and fixed. It's not just some abstract electrical theory; it's practical knowledge that can help you understand and maintain your home's electrical system.
So, stick around as we shine a light on the crucial role of parallel circuits (noun) in residential electrical wiring! We'll explore the differences between series and parallel setups, why parallel is the preferred choice, and what it all means for your daily life. Prepare to have your electrical knowledge powered up!
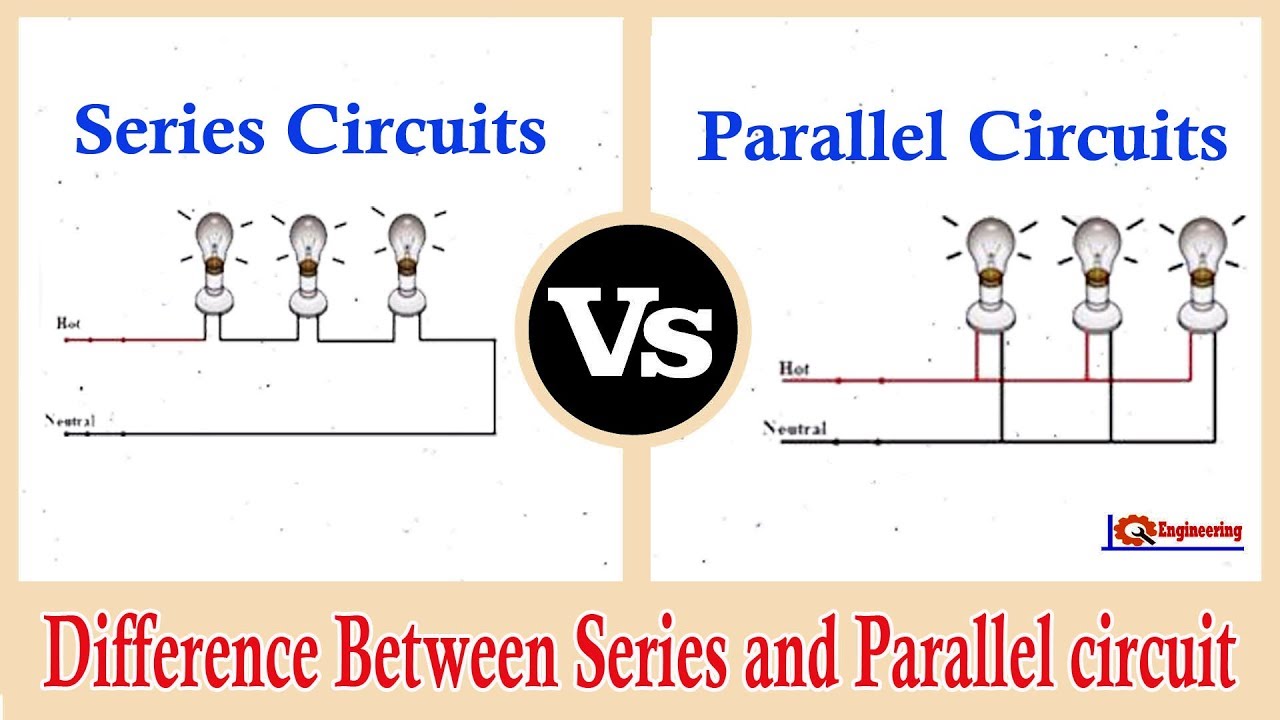
Difference Between A Series And Parallel Circuit
Series Circuits
2. The Perils of a Series Setup
Imagine a string of Christmas lights, where each bulb is connected one after the other in a single loop. That's a series circuit in a nutshell. The current has only one path to flow, meaning it has to go through every single component in the circuit, one after the other. Sounds simple enough, right? Well, here's where the problems begin.
The biggest drawback of series circuits is their vulnerability. If one component in the circuit fails — say, a bulb burns out — the entire circuit is broken. The current can no longer flow, and everything connected to that circuit shuts down. Remember those frustrating moments when you had to check every single bulb on that Christmas light string to find the culprit? That's the series circuit blues in action.
Another issue with series circuits is that the voltage is divided among all the components. This means each device receives only a fraction of the total voltage, which can lead to dim lighting or reduced performance, especially if there are many devices connected in series. It's like trying to share a single slice of pizza among a large group of hungry people — everyone gets a tiny, unsatisfying bite.
Because of these limitations, series circuits are rarely used for general wiring in homes. They are better suited for applications where a single path is desired and the failure of one component must halt the whole system, such as certain types of safety circuits. But for powering your living room, kitchen, and everything in between, a more reliable solution is needed.

Real Life Applications Of Series And Parallel Circuits Wiring Way
Parallel Circuits
3. The Advantages of a Parallel System
Unlike series circuits, parallel circuits offer multiple paths for the current to flow. Think of it like a network of highways instead of a single, winding road. Each appliance or light fixture in your home has its own dedicated pathway back to the power source. This arrangement provides several key advantages.
The most important advantage of parallel circuits (noun) is that if one device fails, the others keep working. If a light bulb burns out in your living room, it won't plunge the entire house into darkness. This is because the other devices have their own separate paths to the power source and are not affected by the failure of one component. It's like having multiple backup plans in case one fails.
Another major benefit is that each device receives the full voltage from the power source. This ensures that all your appliances and lights operate at their optimal performance. You won't have to worry about dim lights or sluggish appliances due to voltage drops. Each device gets its full share of the electrical pie, resulting in consistent and reliable performance.
Finally, parallel circuits make it easier to isolate and fix problems. Because each device is on its own branch, you can quickly identify and address issues without affecting the rest of the electrical system. It's like having clearly labeled sections in a cookbook, making it easier to find the recipe you need without flipping through the entire book. This makes troubleshooting and repairs much simpler and more efficient.
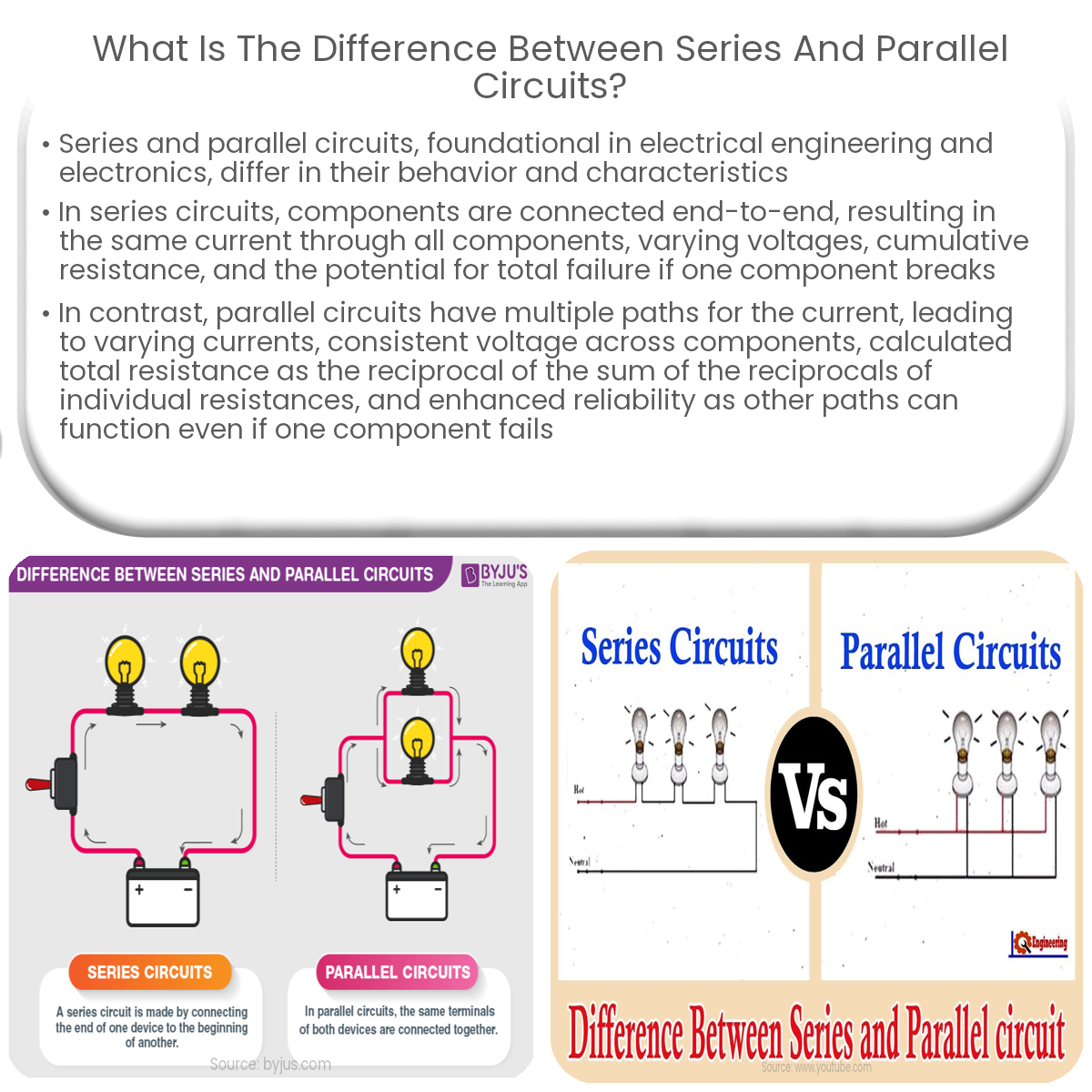
Why Parallel Circuits Reign Supreme in Homes
4. A Home Wired for Success
The reasons why homes use parallel circuits (noun) should be clear now, but let's make it explicitly clear. It is because of reliability, voltage consistency, and ease of troubleshooting. These benefits make them the ideal choice for powering the diverse range of appliances and devices found in a modern home. Imagine trying to run your refrigerator, TV, and computer on a series circuit — the slightest hiccup in one device could bring everything crashing down.
The parallel configuration ensures that each device receives the power it needs without impacting the others. This is crucial for maintaining the comfort and convenience of modern living. From keeping your food cold to ensuring your lights are bright, parallel circuits play a vital role in powering your daily life. They are the unsung heroes of the electrical world, working silently behind the scenes to keep everything running smoothly.
While it's rare to find series circuits used for general wiring in homes, they might be used in specific applications, such as certain types of safety devices or specialized equipment. However, the vast majority of your home's electrical system relies on the robust and reliable nature of parallel circuits. So the next time you flip a switch or plug in an appliance, remember the magic of parallel circuits at work!
Knowing the difference between series and parallel circuits can also help you understand how to safely use electricity and troubleshoot minor electrical problems. While it's always best to consult a qualified electrician for any major issues, having a basic understanding of your home's electrical system can empower you to make informed decisions and take better care of your home.

Understanding Amperage and Your Home's Circuits
5. Staying Safe and Avoiding Overload
Now that we've established that your home uses parallel circuits, let's talk about something equally important: amperage. Amperage is the measure of electrical current flowing through a circuit, and it's crucial for preventing overloads and ensuring safety. Every circuit in your home has a maximum amperage rating, typically 15 or 20 amps.
When you plug in multiple devices to a single circuit, the current drawn by each device adds up. If the total current exceeds the circuit's amperage rating, it can cause the circuit breaker to trip, cutting off power to that circuit. This is a safety mechanism designed to prevent overheating and potential fires. Think of it as the electrical system's built-in safeguard.
To avoid overloading circuits, it's important to be mindful of the power consumption of the devices you're using. High-power appliances like hair dryers, space heaters, and microwave ovens draw a significant amount of current and should ideally be plugged into dedicated circuits. Avoid plugging multiple high-power appliances into the same outlet or circuit, as this can easily cause an overload.
Understanding amperage and circuit ratings can help you use electricity safely and efficiently in your home. By being aware of the power consumption of your devices and avoiding overloads, you can prevent electrical problems and ensure the long-term reliability of your home's electrical system. It's all about being informed and making smart choices when it comes to using electricity.

FAQ
6. Common Circuit Queries
Still have some burning questions about circuits and electricity in your home? Here are a few frequently asked questions to further illuminate the subject:
Q: What happens if I overload a circuit?A: If you overload a circuit, the circuit breaker will trip, cutting off power to that circuit. This is a safety mechanism to prevent overheating and potential fires. To restore power, simply unplug some devices and reset the circuit breaker.
Q: How can I tell if a circuit is overloaded?A: Common signs of an overloaded circuit include flickering lights, warm outlets, and the circuit breaker tripping frequently. If you notice any of these signs, it's a good idea to unplug some devices and consult with an electrician if the problem persists.
Q: Can I add more outlets to an existing circuit?A: Adding more outlets to an existing circuit can be risky, especially if the circuit is already heavily loaded. It's best to consult with an electrician to determine if the circuit can handle the additional load and to ensure that the wiring is up to code.